Virtualization is a technique of how to separate a service from the underlying physical delivery of that service. It is the process of creating a virtual version of something like computer hardware. It was initially developed during the mainframe era. It involves using specialized software to create a virtual or software-created version of a computing resource rather than the actual version of the same resource. With the help of Virtualization, multiple operating systems and applications can run on same machine and its same hardware at the same time, increasing the utilization and flexibility of hardware.
In other words, one of the main cost effective, hardware reducing, and energy saving techniques used by cloud providers is virtualization. Virtualization allows to share a single physical instance of a resource or an application among multiple customers and organizations at one time. It does this by assigning a logical name to a physical storage and providing a pointer to that physical resource on demand. The term virtualization is often synonymous with hardware virtualization, which plays a fundamental role in efficiently delivering Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS) solutions for cloud computing. Moreover, virtualization technologies provide a virtual environment for not only executing applications but also for storage, memory, and networking.
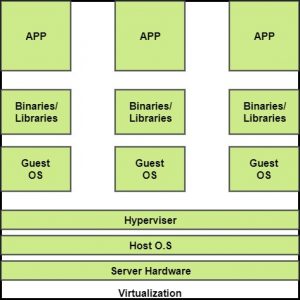
The machine on which the virtual machine is going to be build is known as Host Machine and that virtual machine is referred as a Guest Machine.
BENEFITS OF VIRTUALIZATION
1.More flexible and efficient allocation of resources.
2.Enhance development productivity.
3.It lowers the cost of IT infrastructure.
4.Remote access and rapid scalibility.
5.High availability and disaster recovery.
6.Pay per use of the IT infrastructure on demand.
7.Enables running multiple operating system.
Types of Virtualization:
1.Application Virtualization.
2.Network Virtualization.
3.Desktop Virtualization.
4.Storage Virtualization.

1. Application Virtualization:
Application virtualization helps a user to have a remote access of an application from a server. The server stores all personal information and other characteristics of the application but can still run on a local workstation through internet. Example of this would be a user who needs to run two different versions of the same software. Technologies that use application virtualization are hosted applications and packaged applications.
2. Network Virtualization:
The ability to run multiple virtual networks with each has a separate control and data plan. It co-exists together on top of one physical network. It can be managed by individual parties that potentially confidential to each other.
Network virtualization provides a facility to create and provision virtual networks—logical switches, routers, firewalls, load balancer, Virtual Private Network (VPN), and workload security within days or even in weeks.
3. Desktop Virtualization:
Desktop virtualization allows the users’ OS to be remotely stored on a server in the data center. It allows the user to access their desktop virtually, from any location by different machine. Users who wants specific operating systems other than Windows Server will need to have a virtual desktop. Main benefits of desktop virtualization are user mobility, portability, easy management of software installation, updates and patches.
4. Storage Virtualization:
Storage virtualization is an array of servers that are managed by a virtual storage system. The servers aren’t aware of exactly where their data is stored, and instead function more like worker bees in a hive. It makes managing storage from multiple sources to be managed and utilized as a single repository. storage virtualization software maintains smooth operations, consistent performance and a continuous suite of advanced functions despite changes, break down and differences in the underlying equipment.





0 comments:
Post a Comment